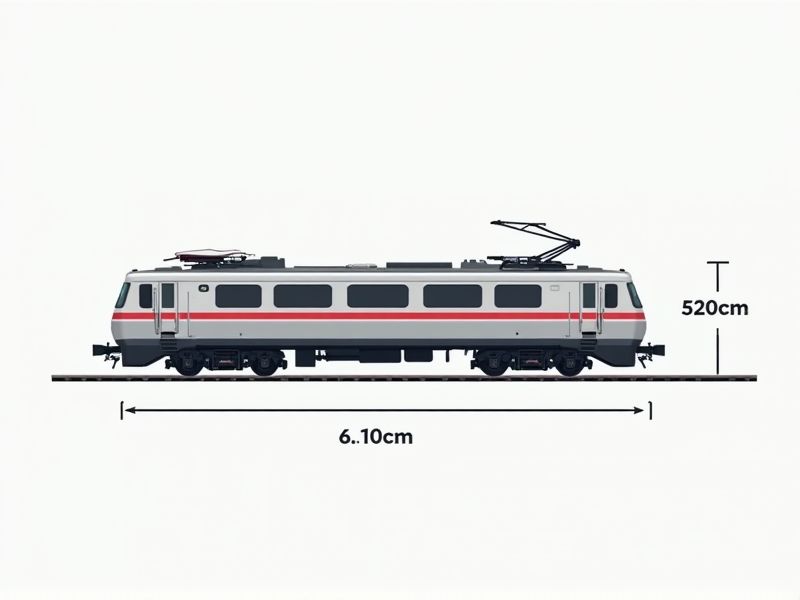
Understanding the standard dimensions of a train can be helpful whether you're planning model layouts or working in transportation design. Typically, a standard passenger train car is about 25 meters (82 feet) long, 3 meters (10 feet) wide, and around 4 meters (13 feet) tall. Freight trains, however, may have cars of varying sizes depending on the cargo, but the width and height often remain similar to ensure compatibility with tunnels and platforms. Always check the specific rail operator's guidelines, as dimensions can vary slightly depending on country or rail system.
Track Gauge
Track gauge is a critical standard in railway systems, referring to the distance between the inner sides of the two parallel rails. The most widely used track gauge worldwide is 1,435 mm, known as the standard gauge, which facilitates interoperability among trains in different regions. Variations exist, such as broad gauge (1,668 mm) and narrow gauge (1,000 mm), each influencing train speed, stability, and capacity. Maintaining the correct track gauge ensures optimal safety and efficiency in train operations, impacting both passenger experience and freight transport.
Platform Height
The standard platform height for trains in most countries typically ranges from 38 inches (97 cm) to 48 inches (122 cm) above track level, ensuring accessibility for passengers. This height accommodates various train designs, reducing the gap between the train and platform for safer boarding. Modern train systems often implement adjustable platform heights to cater to different train models, improving the overall passenger experience. Consider the implications for your local transportation system when evaluating accessibility features and infrastructure improvements.
Car Width
Train car width standards typically range from 2.7 meters to 3.4 meters, depending on the region and rail system. In Europe, the standard rail car width is often 2.82 meters, while in North America, it is around 3.05 meters. Adhering to these dimensions ensures compatibility with track gauges and clearances, essential for safe operations. For transit authorities, optimizing car width can enhance passenger capacity without sacrificing comfort.
Car Length
The standard train car length varies significantly, typically ranging from 50 to 85 feet (15 to 26 meters), depending on their intended use. Freight cars often measure around 60 feet (18 meters), while passenger cars usually fall between 72 and 85 feet (22 to 26 meters) long. This variation allows for optimized capacity and efficiency in transporting goods and passengers. Understanding these measurements can enhance your appreciation of the complex design and engineering behind modern train systems.
Car Height
Train car height standards are crucial for ensuring safe operations and compatibility within various rail systems. Typically, standard passenger train cars in the United States have a height of approximately 13 feet and 6 inches, allowing for compatibility with most platforms and tunnel clearances. Freight cars, on the other hand, generally maintain a slightly lower height of around 13 feet, designed to accommodate different cargo types while meeting clearance regulations. You should be aware that exceeding these height limits can lead to increased risk of accidents and operational disruptions.
Axle Load
The standard axle load for freight trains typically ranges from 20 to 25 metric tons per axle, ensuring efficient transportation of goods over various rail networks. This load capacity is vital for calculating track strength, where lighter loads can lead to reduced wear on infrastructure, extending its lifespan. In the United States, the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) sets regulations to maintain safety and performance standards for axle loads, influencing operational efficiency. Understanding these standards is crucial for optimizing your logistics strategies, maximizing load efficiency, and minimizing operational costs.
Coupling System
The coupling system is essential for train operations, ensuring safety and efficiency by connecting multiple carriages securely. Modern trains often utilize air-powered or automatic couplers that can handle loads of up to 1,000 tons, enhancing the ability to transport heavy freight. Regular inspections, typically every 1,000 miles of travel, are necessary to maintain the integrity of these connections and prevent accidents. Understanding the coupling mechanism's specifications, such as the type of coupler and its load-bearing capacity, is crucial for your train's operational safety.
Clearance Envelope
The clearance envelope for trains is defined by a specific distance from the tracks, typically ranging from 3 to 15 feet, ensuring that all structures, including platforms and tunnels, remain safely distanced from passing trains. This safety parameter is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring passenger safety, as it accommodates the dynamic movement of trains and any potential overhang. Regulations often mandate regular inspections of this clearance zone, with particular emphasis on areas where infrastructure and natural obstacles might intrude. Knowing these standards can help you better understand the complexities involved in railway operations and infrastructure planning.
Bogie Dimensions
Bogie dimensions play a crucial role in train stability and performance, with standard measurements typically ranging from 2.5 to 3 meters in width. The axle spacing often measures between 1.8 to 2.5 meters, ensuring weight distribution and reducing wear on tracks. Each bogie supports a weight capacity of around 25 tons, which is essential for heavy freight or passenger service trains. Understanding these specifications can enhance your insights into railway engineering and operational efficiency.
Overhang Limits
Overhang limits are critical in ensuring the safe design and operation of trains, typically defined by the lateral distance a train may extend beyond its track. For example, commuter trains often maintain an overhang limit of approximately 1.6 meters to avoid hazards near platforms and other railway structures. Regulatory bodies like the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) set stringent guidelines that must be followed to ensure passenger safety and minimize risks during train operations. By adhering to these standards, rail operators can effectively manage the balance between train design efficiency and passenger safety.
