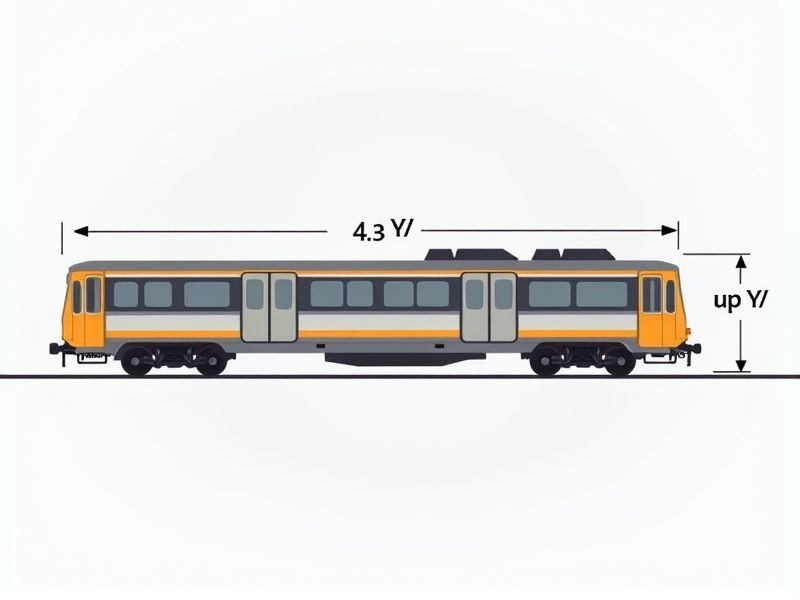
The standard dimensions of a typical subway car can vary slightly depending on the city and train model, but most subway cars are about 8 to 10 feet wide and 50 to 75 feet long. For example, in the New York City subway system, cars are often around 60 feet long and approximately 9 feet wide, designed to fit within narrow tunnels and accommodate city infrastructure. These dimensions maximize the number of passengers each car can carry while ensuring the train can safely navigate curves and station platforms. Knowing these general measurements can help you plan layouts, model projects, or assess accessibility needs related to subway systems.
Car Length
The standard length of a subway car typically ranges from 60 to 75 feet, depending on the transit system and operational requirements. For instance, most modern metro systems standardize their car lengths to optimize passenger capacity and train formation efficiency. A longer subway car can accommodate more passengers; thus, systems like New York City's R160 model, measuring approximately 75 feet, allow for effective crowd management during peak hours. Choosing the right car length is crucial for maintaining a balance between operational efficiency and passenger comfort.
Car Width
The standard width of a subway car typically ranges from 8.5 to 10 feet, with variations depending on the city and system specifications. A wider car provides increased passenger capacity, allowing up to 200 individuals per vehicle during peak hours. Maintaining a consistent car width is essential for seamless integration into existing platforms and infrastructure, ensuring safety and accessibility for all riders. In cities like New York, car width is critical to accommodate the high volume of daily commuters, which exceeds 5 million passengers on average.
Car Height
Subway car heights typically range between 10 to 12 feet, ensuring compatibility with most subway systems worldwide. This dimension plays a crucial role in maximizing passenger capacity while minimizing aerodynamic drag during operation. With over 5,000 subway cars in major cities, uniform height standards help maintain efficient train operations and platform access. Proper car height is essential for safety features, such as emergency exits and wheelchair accessibility, enhancing the overall user experience.
Interior Seating Capacity
The interior seating capacity of standard subway cars typically ranges from 60 to 80 seats, designed to maximize space while ensuring passenger comfort. Each subway car usually accommodates around 150 to 200 passengers when including standing capacity, allowing for efficient use during peak hours. With an average length of approximately 75 feet, the design incorporates ergonomic seating and vertical poles to optimize passenger flow and safety. You can expect features like foldable seats in select areas to enhance accessibility, especially during high-traffic times.
Door Width
The standard width for subway car doors typically measures 28 to 30 inches, accommodating the efficient flow of passengers. This dimension allows for the quick boarding and alighting of approximately 1,200 passengers per hour during peak times. Accessible design mandates often require certain doors to be a minimum of 32 inches wide to ensure compliance with ADA regulations. Ensuring proper door width is crucial not only for passenger comfort but also for improving overall transit system efficiency and safety.
Aisle Width
The standard aisle width in subway cars typically measures between 28 to 36 inches, ensuring adequate space for passenger flow. A wider aisle significantly enhances safety during rush hours, accommodating higher volumes of commuters, which can exceed 1,000 passengers per car during peak times. Designing for optimal aisle width not only improves accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges but also facilitates smooth boarding and disembarking. Your comfort and safety are prioritized through these design standards, further underscoring the importance of efficient urban transportation systems.
Track Gauge Consistency
Track gauge consistency in subway systems is critical for ensuring passenger safety and operational efficiency. Most subway systems operate on a standard gauge of 1,435 mm (4 ft 8.5 in), but variations can exist, impacting interconnectivity and maintenance. Regular inspections and adherence to regulatory standards are essential, as even minor deviations can affect train stability and performance. For optimal safety and reliability, subway car designs integrate advanced technologies to monitor track conditions and maintain uniform gauge adherence.
Weight Limit Per Axle
The weight limit per axle for subway cars typically ranges from 33,000 to 40,000 pounds, depending on the manufacturer and design specifications. This limit ensures the structural integrity of tracks and supports safe operation at high speeds. Many transit authorities regularly conduct inspections to validate adherence to these weight restrictions, which helps prevent accidents and prolongs infrastructure lifespan. You should be aware that exceeding this limit can lead to increased wear on the rail system, affecting reliability and maintenance costs.
Compatibility With Platform Height
Subway car standards emphasize the importance of compatibility with platform heights to ensure safe and efficient passenger boarding and alighting. According to the American Public Transportation Association (APTA), a typical platform height ranges from 34 to 36 inches above the rail, which is designed to align with various subway car floor heights. This compatibility minimizes the need for additional steps or ramps, enhancing accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges. Your city's subway system can benefit from adhering to these standards, potentially improving overall ridership and user satisfaction.
Turning Radius Capability
The turning radius capability of subway cars plays a critical role in urban transit efficiency, particularly in densely populated areas. Modern subway systems often require a minimum turning radius of around 50 to 70 feet to navigate sharp bends while maintaining passenger comfort and safety. Manufacturers design cars with advanced articulation systems to minimize the stress on track infrastructure, which helps enhance the longevity of rails and overall operational reliability. Your understanding of this specification affects matters like crowding and scheduling, directly impacting the satisfaction of riders in major metropolitan networks.
