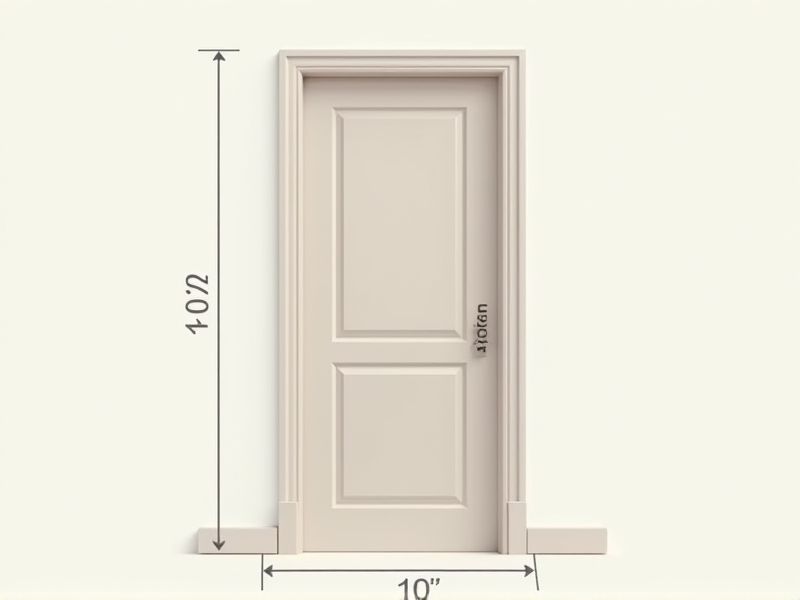
The standard dimensions of a residential door are typically 80 inches (6 feet 8 inches) in height and 36 inches (3 feet) in width. However, some doors may be 30 or 32 inches wide, depending on their intended use or local building codes. The standard thickness for most interior and exterior doors is about 1 3/8 inches and 1 3/4 inches, respectively. Knowing these dimensions is useful when planning renovations, purchasing replacement doors, or ensuring compliance with accessibility requirements.
Width
The standard width of a residential door typically measures 36 inches, providing ample space for accessibility and ease of movement. Some interior doors may range from 28 to 32 inches in width, catering to various room dimensions and design aesthetics. By utilizing the standard width, you ensure compliance with building codes and improve flow within your home. If you're planning door installations or renovations, confirming these measurements is essential for achieving optimal functionality and style.
Height
The standard height for residential interior doors is typically 80 inches, or 6 feet 8 inches. This measurement is essential for ensuring optimal accessibility and aesthetics within the space. For specialized applications, such as commercial buildings or unique designs, door heights can vary, reaching up to 96 inches or 8 feet. Consider your ceiling height and overall room proportions when selecting a door to maintain harmony in your interior design.
Thickness
The standard door thickness typically ranges from 1 3/8 inches to 1 3/4 inches, depending on the type and purpose of the door. A thickness of 1 3/4 inches is commonly used for exterior doors, providing enhanced durability and security. Interior doors usually measure 1 3/8 inches, balancing aesthetics with functionality. Choosing the right thickness is crucial for insulation, soundproofing, and overall performance in your space.
Material
The standard door typically utilizes materials such as solid wood, hollow core, or steel, with wood providing natural insulation and aesthetic appeal. Solid wood doors generally offer superior durability and heightened security, while hollow core doors are lightweight and cost-effective, often used in interior spaces. Steel doors enhance safety and are often preferred for exterior applications due to their resistance to weather elements and potential intrusions. When choosing the right door for your needs, consider factors such as thermal performance, maintenance requirements, and sound insulation properties.
Panel Design
A standard door typically features a panel design that enhances both aesthetic appeal and functionality. Panel configurations can vary, with the most common being three or four panels, each contributing to the overall structure and insulation of the door. The use of various materials, such as solid wood, fiberglass, or steel, impacts not only durability but also energy efficiency, with R-values ranging from 3 to 8. When selecting a door, consider how the panel style complements your home's architecture and your personal design preferences.
Swing Direction
The standard door typically swings inwards or outwards, with the swing direction significantly impacting space utilization and accessibility. For residential doors, the most common swing direction is outwards, allowing for easier movement into smaller areas. In commercial settings, doors often swing towards the foot traffic, ensuring a seamless flow in high-traffic environments. When selecting a door, consider how its swing direction will affect your room layout and overall functionality.
Frame Size
The standard door frame size typically measures 80 inches in height and 36 inches in width, accommodating a variety of residential and commercial spaces. A properly fitted frame is crucial for ensuring energy efficiency and preventing drafts. You should consider the wall thickness, which often ranges from 4.5 inches to 6 inches, to select an appropriate door frame that complements your structure. Depending on your specific needs, frames can be made from materials such as wood, steel, or fiberglass, offering varying durability and aesthetic appeal.
Clear Opening Size
The standard door typically emphasizes a clear opening size of 32 inches wide and 80 inches high, which ensures accessibility for individuals, including those with disabilities. This dimension meets the guidelines set by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), allowing wheelchair users ample space to enter and exit. To enhance accessibility, consider installing doors with a minimum width of 36 inches when possible, as this facilitates smoother navigation. Proper installation of standard doors also involves maintaining a threshold height of no more than 1/2 inch for seamless entry.
Threshold Height
The standard threshold height for residential doors commonly measures between 1.5 to 2 inches, ensuring a proper seal against moisture and drafts. Your choice of threshold can significantly affect energy efficiency, with more insulated options yielding better temperature control. Industry guidelines suggest that thresholds should not only meet local building codes but also accommodate accessibility standards when necessary. Regular maintenance of door thresholds helps prolong their lifespan and maintains optimal performance for years.
Jamb Depth
The standard door jamb depth typically measures 4 9/16 inches, essential for accommodating a variety of wall thicknesses. This depth ensures proper alignment and installation of the door within the frame, enhancing durability and functionality. You may encounter jambs with varying depths, such as 4 3/4 inches for thicker walls or specific architectural styles. Selecting the correct jamb depth not only improves aesthetic appeal but also affects energy efficiency and soundproofing within your space.
