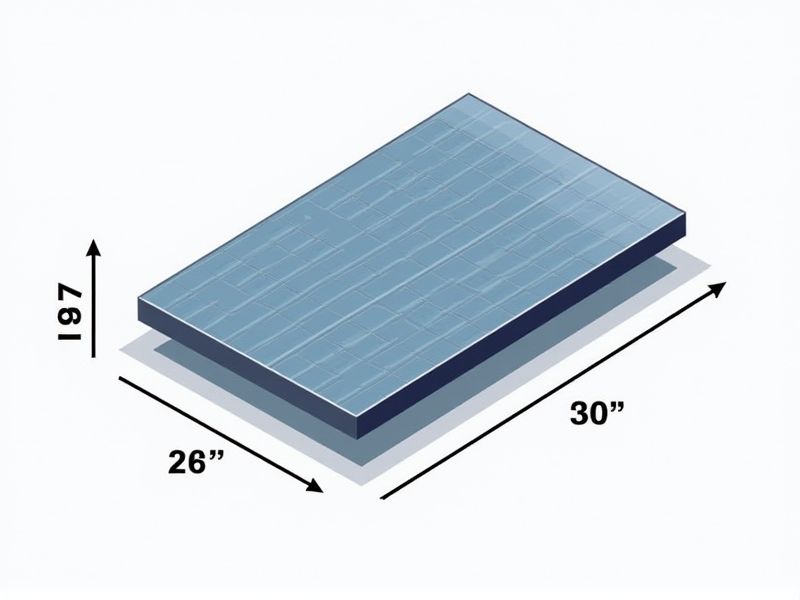
When considering solar panels for your home or business, it's helpful to know the standard dimensions for efficient planning and installation. Most typical residential solar panels measure around 65 inches by 39 inches (approximately 5.4 feet by 3.25 feet), while commercial panels are often larger, usually about 78 inches by 39 inches. A standard panel is usually 1.5 to 2 inches thick, with weight commonly ranging from 40 to 50 pounds. Knowing these dimensions can help you accurately assess your available roof space and design the optimal solar energy system for your needs.
Length
The standard length of solar panels typically measures around 65 to 70 inches, which corresponds to most residential and commercial installations. This length is designed to maximize efficiency by ensuring an adequate surface area to capture sunlight effectively. On the other hand, larger commercial panels can reach up to 100 inches, enhancing their power output capacity. Your choice of panel size can significantly impact the overall energy yield and installation requirements for any solar energy project.
Width
The standard width of solar panels typically ranges from 39 to 40 inches, influencing installation and efficiency. Most residential panels measure around 65 inches in length, allowing for optimal space utilization on rooftops. Each panel can produce between 250 to 400 watts, depending on its size and technology. You should consider the width of the panels when planning your solar energy system to ensure effective sunlight exposure and maximize energy generation.
Thickness
The thickness of solar panels typically ranges from 0.15 to 0.50 inches, influencing both efficiency and durability. Thinner panels, around 0.15 inches, are lightweight and flexible, making them suitable for diverse applications but may compromise on longevity. In contrast, thicker panels, approaching 0.50 inches, offer enhanced stability and resistance to environmental factors like hail and wind. Selecting the right thickness can significantly impact energy production, with most standard panels exhibiting an efficiency rating between 15% and 22%, depending on material and thickness choices.
Weight
The standard weight of a solar panel typically ranges from 40 to 50 pounds (18 to 23 kilograms) for a traditional 60-cell model. This weight is crucial for installation, as it influences roof load capacity and the choice of mounting systems. Lightweight solar panels, which often weigh around 30 pounds (14 kilograms), are available and may be beneficial for specific applications or structures. Considering weight in your solar panel selection can enhance the efficiency and practicality of your renewable energy solution.
Frame Material
The frame material of solar panels significantly impacts their durability and overall performance. Most high-quality solar panels utilize anodized aluminum frames, known for their lightweight yet robust characteristics, providing a lifespan that often exceeds 25 years. In contrast, cheaper options may use plastic or lower-grade metals, which can compromise both strength and resistance to environmental factors like corrosion. When selecting solar panels, prioritizing those with durable and corrosion-resistant frame materials ensures enhanced longevity and reliability for your energy production.
Cell Configuration
The standard cell configuration of solar panels plays a crucial role in determining their efficiency and overall performance. Most commonly, solar panels utilize monocrystalline or polycrystalline cells, with efficiency rates ranging from 15% to 22%. A typical solar panel consists of 60 or 72 cells, which influences the panel's output power, generally between 250 and 400 watts. Understanding these configurations allows you to choose the right solar panel system for your energy needs, potentially leading to significant cost savings on electricity bills.
Mounting Holes
Modern solar panels typically feature mounting holes that accommodate a standard spacing of 40 to 45 inches apart, ensuring stability and easy installation. These mounting holes are often designed to handle wind loads of up to 140 mph, making them suitable for various weather conditions. With a standard panel size of approximately 65 inches by 39 inches, proper alignment of these holes is crucial for maximizing energy efficiency. When installing your solar panel system, attention to the positioning and securing of these mounting holes can significantly enhance durability and performance over time.
Junction Box Size
The junction box size of a solar panel significantly influences its efficiency and performance, typically measuring between 100 mm x 100 mm to 150 mm x 150 mm. A well-designed junction box accommodates essential components such as bypass diodes, which enhance energy output by preventing power loss under shaded conditions. Furthermore, the IP rating of the junction box, commonly IP65 or IP67, ensures adequate protection against dust and water ingress, contributing to the panel's durability. Selecting a solar panel with an appropriately sized junction box can optimize your system's longevity and overall energy yield.
Connector Type
Connector type is crucial for the efficient installation and performance of solar panels, affecting both energy production and durability. Common connector types include MC4, Amphenol, and Tyco, each designed for easy and secure connections that can withstand outdoor elements. Proper selection of the connector ensures compatibility with various inverters and systems, as well as optimal conductivity which can reduce energy loss by up to 5%. Ensuring your solar panels have the right connector type can enhance system reliability and longevity, making it a key factor in your investment.
Glass Type
Solar panels typically utilize three main types of glass: tempered, low-iron, and anti-reflective. Tempered glass offers robust durability, boasting a strength up to five times that of standard glass, which enhances the panel's resistance to impact and environmental stress. Low-iron glass increases light transmission, allowing up to 91% more sunlight to reach the solar cells, thereby improving overall efficiency. Anti-reflective coatings can further boost energy output by reducing glare, ensuring that your solar system operates at its peak performance.
