Radiators come in a variety of standard dimensions to suit different heating needs and room sizes. For example, typical panel radiators for homes are often available in heights ranging from 300mm to 600mm (approximately 12 to 24 inches), with common widths of 400mm to 2000mm (around 16 to 79 inches). The thickness can vary depending on whether it is a single, double, or triple panel, generally between 50mm and 160mm. When selecting a radiator, it's important to measure your available wall space and consider your room's heating requirements to ensure an optimal fit and efficient performance.
Core Height
The core height of a radiator is a critical factor affecting its efficiency and heating performance. Typically, radiators are available with core heights ranging from 300 mm to 900 mm, with the most common dimension being around 600 mm. A higher core height allows for greater surface area, improving heat distribution and ensuring faster room warming. When selecting a radiator, consider your space's specific heating requirements to optimize thermal output effectively.
Core Width
The core width of a radiator significantly influences its heat output and efficiency. Typical core widths range from 1.5 inches to 3 inches, with wider cores generally providing better thermal performance. For optimal heating, select a radiator with a core width tailored to your room size; larger spaces benefit from wider cores to enhance heat distribution. Evaluating the core width in relation to your heating needs can lead to improved energy efficiency and comfort in your home.
Core Thickness
The standard for radiator performance is significantly influenced by core thickness, which directly impacts heat dissipation efficiency. A typical core thickness ranges from 25mm to 50mm, with thicker cores generally providing better thermal conductivity. Radiator core thickness not only affects the heat exchange process but also dictates airflow resistance, which can impact overall vehicle cooling performance. Evaluating your vehicle's specifications can help determine the optimal core thickness needed for improved engine cooling and longevity.
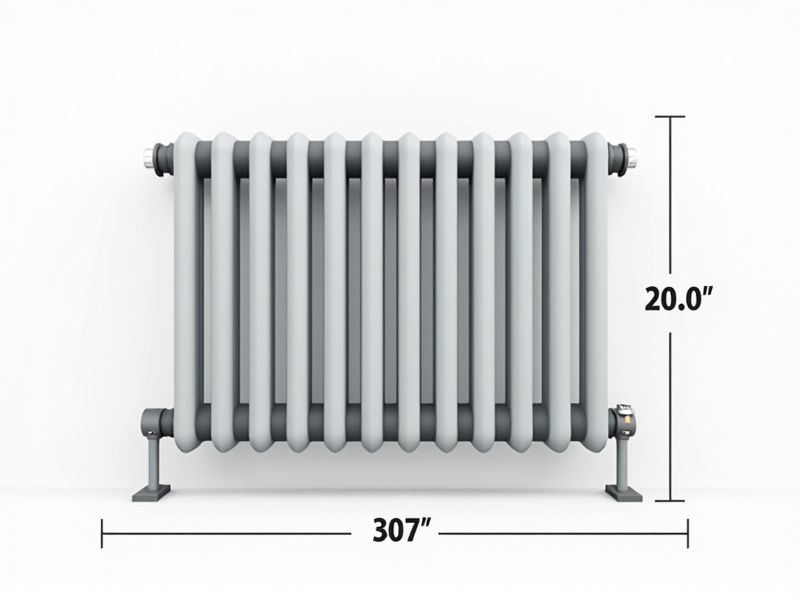
Overall Height
The overall height of a radiator typically ranges from 400 mm to 1800 mm, catering to various room sizes and design preferences. A taller radiator often provides more heat output, making it ideal for larger spaces or rooms with high ceilings. When selecting a radiator, consider how the overall height complements your existing decor and layout, ensuring it fits comfortably without overwhelming the space. Choosing the right height can enhance both the functionality and aesthetic appeal of your heating solution.
Overall Width
The overall width of a radiator significantly influences its heating efficiency and compatibility with your space. Standard radiators vary in width, typically ranging from 400 mm to 3000 mm, allowing for diverse installation options in residential and commercial settings. Wider models often provide increased surface area, leading to improved heat distribution and faster warming of the room. When selecting a radiator, consider the overall width to ensure it meets your heating requirements while fitting seamlessly into your interior design.
Overall Depth
The overall depth of a radiator is crucial for effective heat distribution in your space, typically ranging from 3 to 12 inches depending on the model. A deeper radiator can hold more water, enhancing its thermal efficiency and heating output, which is essential for larger rooms or colder climates. Standard depth measurements often correlate with the radiator's BTU (British Thermal Units) rating, influencing its capacity to heat an area efficiently. For optimal results, consider your room's dimensions and insulation when selecting the appropriate radiator depth.
Tube Length
The standard tube length for radiators typically ranges from 1.25 meters to 3 meters, depending on the specific application and design requirements. A longer tube length can significantly enhance the heat output, averaging up to 1,500 watts per linear meter. When selecting a radiator, consider that a 2-meter tube may cover a room of approximately 30 square meters efficiently. Ensuring optimal installation with the correct tube length can lead to improved energy efficiency and comfort in your space.
Fin Density
The fin density of a radiator is a critical factor that influences its heat exchange efficiency, typically measured in fins per inch. Higher fin density enhances the surface area, allowing for improved heat dissipation, which is essential for maintaining optimal engine temperatures. For example, radiators with a fin density exceeding 12 fins per inch can significantly increase thermal performance compared to standard models. You should consider this metric when selecting a radiator to ensure it meets your vehicle's cooling requirements effectively.
Inlet And Outlet Diameters
The standard radiator typically features inlet and outlet diameters that range from 3/4 inch to 1 inch, depending on the system requirements. These dimensions are crucial as they affect the flow rate and efficiency of the heating or cooling process. For optimal performance, ensure the inlet and outlet connections match the specifications outlined in your heating system's design. Choosing the correct diameter can significantly enhance thermal conductivity and overall system reliability.
Mounting Hole Spacing
Mounting hole spacing for radiators is crucial for proper installation and compatibility with various systems. Standard spacing typically ranges from 300 mm to 600 mm, accommodating most residential and commercial setups. Ensuring your radiator aligns with these measurements can significantly enhance efficiency and performance. This attention to detail not only ensures optimal heat distribution but also simplifies maintenance over time.
