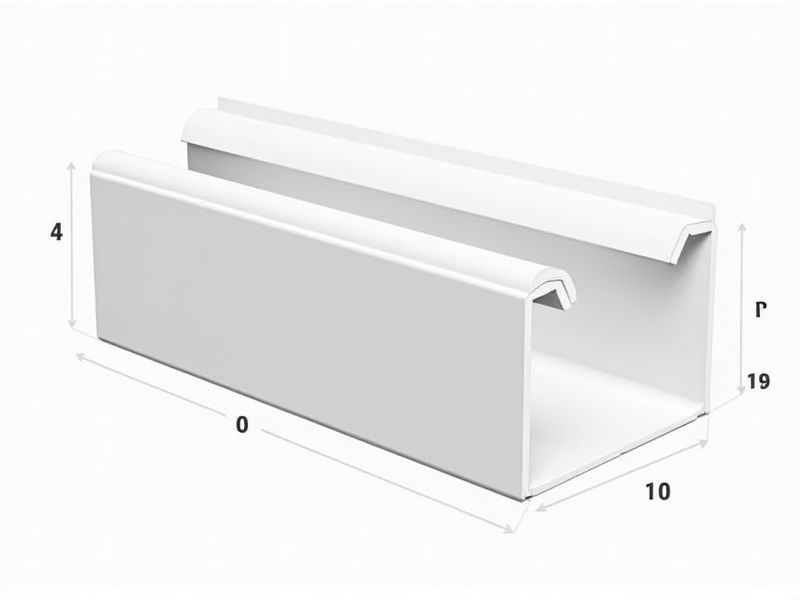
When selecting gutters for a home or building, it's important to know the standard dimensions most commonly used. Typically, residential gutters come in widths of 5 or 6 inches, with 5-inch K-style gutters being the most popular option for homes. Downspouts usually measure 2x3 inches or 3x4 inches, depending on the gutter size and your area's rainfall volume. Choosing the right dimension ensures optimal water drainage and protects your property from potential water damage.
Width Specifications
Gutter width specifications typically range from 4 to 6 inches, ensuring efficient water flow and debris management. A 5-inch gutter is ideal for average rainfall areas, while 6-inch gutters provide enhanced capacity in regions with heavier precipitation. The width directly impacts the gutter's ability to handle water volume, with wider gutters offering better performance during storms. Choosing the correct width based on local weather patterns is crucial for prolonging the lifespan of your gutter system and preventing overflow-related damage.
Depth Measures
The standard of gutter depth measures typically ranges between 4 to 6 inches, depending on the specific requirements of rainfall intensity in your region. Proper gutter depth ensures effective water collection and drainage, reducing the risk of overflow and potential damage to your property. For high-capacity systems, depths of 6 to 8 inches are often recommended, catering to areas with heavier precipitation. Accurate gutter measurement not only improves structural integrity but also enhances your home's aesthetic appeal by maintaining clean lines and effective water management.
Slope Requirements
The standard slope requirement for gutters is typically set between 1% to 2%, ensuring effective drainage for rainwater. This means that for every 10 to 12 feet of the gutter, there should be a drop of at least 1 to 2 inches towards the downspout. Proper slope maintenance helps prevent water pooling, which can lead to mold growth and structural damage. You should regularly inspect your gutters to ensure they meet these slope standards for optimal performance.
Material Types
Gutter materials primarily include aluminum, vinyl, copper, and galvanized steel, each offering distinct advantages. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to rust, making it a popular choice for homeowners, while vinyl gutters are cost-effective and easy to install. Copper gutters provide a classic aesthetic and longevity, often lasting over 100 years with proper maintenance. Galvanized steel gutters, known for their durability, can withstand harsh weather conditions but may require regular maintenance to prevent rusting.
Length Constraints
Gutter standards typically emphasize length constraints, specifically aiming for a minimum width of 1.5 inches to effectively manage water runoff. In residential properties, the recommended length for seamless gutters is often 20 to 30 feet, reducing the number of joints and minimizing potential leaks. For commercial buildings, longer spans may be utilized, depending on the roof structure and regional rainfall patterns. Ensuring your gutters conform to these specifications can significantly enhance drainage efficiency and extend their lifespan.
Downspout Dimensions
The standard downspout dimensions typically range from 2 to 3 inches in width and 3 to 4 inches in depth, ensuring efficient water flow. For optimal performance, downspouts should be installed at intervals of 30 to 40 feet along the gutter system. A properly sized downspout can handle rainfall intensities up to 1.5 inches per hour. You may also consider installing larger downspouts in areas prone to heavy rainfall to prevent overflow and potential damage.
Gutter Style Variations
Gutter style variations significantly influence water drainage and aesthetic appeal in residential and commercial architecture. Common styles include K-style, which features a flat bottom and a rounded front, and half-round, known for its semicircular shape that enhances visual interest. In North America, the standard gutter size typically measures 5 inches, though 6-inch options are available for greater flow capacity in areas prone to heavy rainfall. Choosing the right gutter style can improve functionality and complement your building's design.
Minimum Drainage Capacity
The minimum drainage capacity of gutters is crucial, as it directly affects water management and prevents potential property damage. Typically, a standard residential gutter should accommodate at least 600 square feet of roof area per lineal foot. In regions with heavy rainfall, consider a minimum capacity of 1,000 gallons per hour to ensure efficient runoff. For optimal performance, your gutter system must be designed to handle local precipitation rates and roof configurations.
Overhang Considerations
The standard gutter design emphasizes overhang considerations, typically requiring a projection of 1 to 2 inches from the roof edge. This overhang ensures that rainwater is directed away from the fascia and prevents potential water damage to your home's structures. Proper installation allows for optimal drainage, minimizing overflow and reducing the risk of clogs in the downspouts. Maintaining a standard overhang also enhances the aesthetic appeal, seamlessly integrating functionality with design elements.
Installation Guidelines
When installing gutters, it is crucial to follow the manufacturer's installation guidelines to ensure proper functionality. Position the gutters at a minimum slope of 1 inch for every 10 feet, facilitating efficient water flow towards downspouts. Secure each section with appropriate hardware, typically every 24 inches, to withstand wind load and prevent sagging. Regular maintenance, including cleaning debris from gutters and downspouts at least twice a year, will prolong their lifespan and enhance drainage efficiency.
