When considering the standard dimensions of a greenhouse, it's important to think about both your available space and your gardening goals. Most home greenhouses are typically around 6 to 10 feet wide and 8 to 20 feet long, with a height of 7 to 8 feet to allow for comfortable movement and plant growth. For example, a popular beginner size might be 6 feet by 8 feet, which provides enough room for several shelves and taller plants. Choosing the right size ensures you have enough space for your plants, proper ventilation, and easy access for maintenance.
Width
The standard greenhouse width typically ranges from 12 to 30 feet, with most commercial structures favoring widths of around 20 feet to optimize space and sunlight exposure. A wider greenhouse allows for better airflow and can accommodate more plants, increasing your overall productivity. Proper width also facilitates accessibility for equipment and maintenance, ensuring that crops remain healthy and manageable. For hobbyists, a width of 12 to 16 feet offers a balance between capacity and ease of use, providing a functional space for various gardening projects.
Length
The standard for greenhouse design emphasizes a length range of 20 to 120 feet, optimizing space for plant growth and maximizing sunlight exposure. Research indicates that longer greenhouses, ranging from 50 to 100 feet, can enhance air circulation and temperature regulation, leading to healthier plants. A greenhouse's length should also consider ventilation requirements, which become critical as size increases; for instance, every 20 feet typically necessitates an additional vent. When planning your greenhouse, remember that the optimal length directly impacts your crop yield and overall efficiency in maintaining controlled environments.
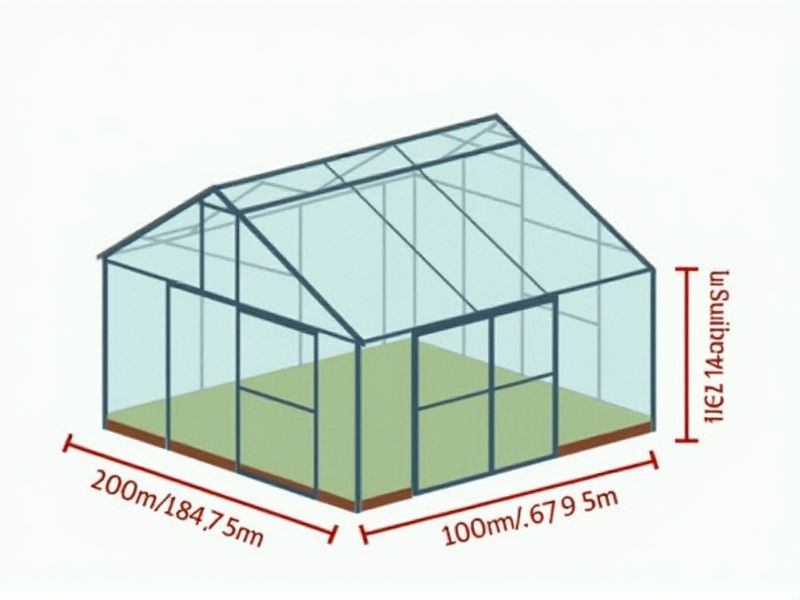
Height
The standard height for a greenhouse typically ranges between 8 to 12 feet, allowing ample space for plants to grow and for proper air circulation. A height of at least 10 feet is ideal for accommodating taller plants and facilitating the installation of ventilation systems. This vertical space not only enhances light distribution but also helps regulate temperature, leading to healthier plant growth. When designing your greenhouse, consider these height standards to optimize your growing conditions and maximize yields.
Roof Pitch
Roof pitch is a critical factor in greenhouse design, influencing both light penetration and water drainage. A roof pitch of 30 degrees is often recommended to maximize sunlight exposure while minimizing the risk of water accumulation. In colder climates, steeper pitches help shed snow, whereas gentler slopes can be more effective in warmer areas to facilitate ventilation. Your choice of roof pitch can ultimately affect plant growth rates and overall greenhouse efficiency.
Ventilation
Proper greenhouse ventilation ensures optimal plant growth and health by maintaining ideal temperature and humidity levels. For a typical greenhouse of 1,000 square feet, it is recommended to use exhaust fans with a capacity of at least 1,000 CFM (cubic feet per minute) to regulate airflow effectively. Natural ventilation methods, such as roof vents and sidewall openings, can provide significant cooling, especially during peak summer months when temperatures can exceed 90degF. Implementing a targeted ventilation strategy can enhance photosynthesis, improve plant respiration, and reduce the risk of mold and disease.
Door Size
The standard greenhouse door size typically ranges from 36 inches to 48 inches in width and 80 inches in height, ensuring easy access for users and equipment. According to industry guidelines, a minimum door height of 80 inches accommodates the needs of taller individuals and equipment, such as carts or wheelbarrows. Adequate door size influences ventilation and pest control, allowing for improved air circulation and easier monitoring of plant health. For optimal functionality, consider the specific needs of your plants and activities when selecting the door size for your greenhouse.
Frame Spacing
Frame spacing in greenhouse structures is crucial for optimizing plant growth and maximizing sunlight exposure. Typically, a spacing of 4 to 6 feet between frames allows for adequate airflow and light penetration, ensuring that plants receive the necessary nutrients. Proper frame spacing can also mitigate the spread of diseases by increasing air circulation around each plant. For your greenhouse, consider using 30-inch wide planting beds with 4-foot aisles to maintain an efficient layout conducive to plant health and harvest productivity.
Foundation Depth
The foundation depth of a greenhouse plays a critical role in ensuring stability and insulation, typically ranging from 12 to 36 inches, depending on local soil conditions and climate. Properly dug foundations help prevent frost heave and moisture accumulation, thus enhancing plant growth and longevity. For you, understanding this depth can significantly impact energy efficiency and pest control within the greenhouse structure. Higher quality designs often incorporate insulated footings, providing additional thermal regulation and stability.
Eave Height
Eave height, measured from the ground to the lowest part of the roof overhang, is a critical factor in greenhouse design, affecting both ventilation and plant growth. The standard eave height typically ranges from 8 to 12 feet, allowing for optimal air circulation and sunlight penetration, which are essential for photosynthesis. Proper eave height can enhance energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss during colder months and reducing heat buildup during the summer. Choosing the right eave height can significantly impact your greenhouse's overall performance and crop yield.
Gutter Height
In greenhouse design, the standard gutter height typically ranges between 12 to 16 feet, ensuring optimal air circulation and lighting for plant growth. This height helps minimize the risk of moisture accumulation while maximizing the efficiency of heat retention during colder seasons. Your choice of gutter height can significantly impact the overall climate control within the greenhouse, affecting factors such as temperature and humidity levels. Ensuring that your greenhouse meets these height standards can lead to improved crop yields and healthier plants.
