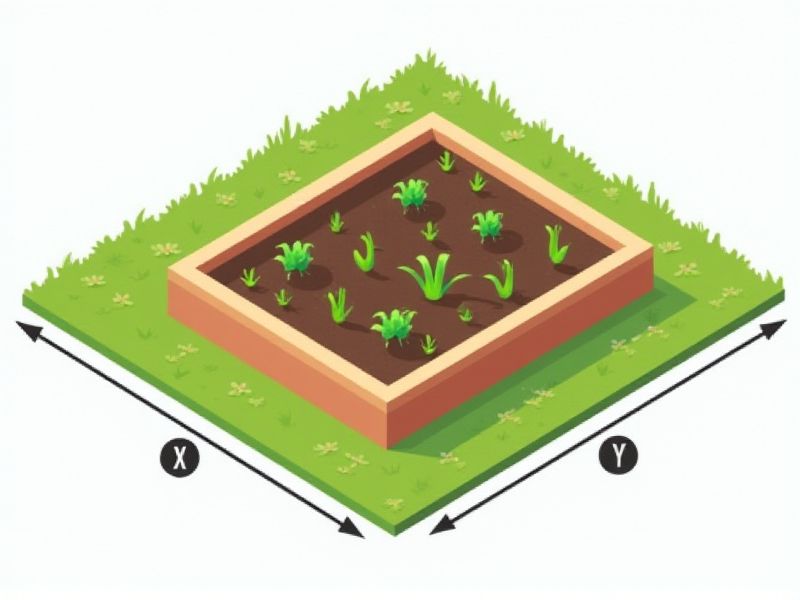
When planning a garden bed, standard dimensions often range from 3 to 4 feet wide and 6 to 8 feet long, with a depth of 12 to 18 inches. This size allows gardeners to easily reach the center of the bed from either side without stepping on the soil, which helps maintain healthy soil structure. For example, a 4-foot by 8-foot bed is both spacious and manageable for most home gardeners. Adjusting the size to fit your available space, needs, and accessibility will help ensure successful gardening results.
Width Consideration
For optimal growth, the standard width of a garden bed typically ranges from 4 to 6 feet. This width allows easy access for maintenance without stepping on the soil, thus preserving its structure and nutrients. Moreover, a narrower bed can ensure better light exposure for plants while promoting efficient irrigation practices. If you aim for a raised garden bed, consider a height of 12 to 24 inches to improve drainage and reduce pest access.
Length Preferences
A standard garden bed typically measures 4 feet in width, allowing for easy access from either side, and varies in length to meet specific gardening needs, commonly ranging from 4 to 12 feet. For optimal plant growth, depth should be at least 12 to 18 inches, providing sufficient soil volume for root development. You can customize the length according to the available space in your yard or garden while ensuring it accommodates your desired plants. When designing your garden bed, consider integrating trellises or support structures for vertical growth, which can maximize your gardening area.
Optimal Depth
An optimal garden bed depth ranges from 12 to 18 inches, allowing for adequate root growth and soil aeration. This depth promotes healthy drainage while retaining moisture, essential for robust plant development. Choosing the right materials for the bed's construction can further enhance soil quality and temperature regulation. A well-designed garden bed with proper depth can significantly increase your vegetable yield by providing a fertile environment for various plants.
Pathway Spacing
The ideal pathway spacing for garden beds typically ranges from 18 to 36 inches, accommodating comfortable access for maintenance and harvesting. A narrower pathway of 18 inches can be efficient for smaller gardens, whereas a broader path of up to 36 inches allows for the use of gardening tools without obstructing neighboring plants. This spacing promotes efficient air circulation and sunlight exposure, essential for optimal plant health. Your garden's layout, including pathway width, significantly influences productivity and ease of care.
Soil Volume Standards
A standard garden bed typically requires a soil volume of at least 2-3 cubic feet per square foot to ensure optimal plant growth. For a raised garden bed measuring 4 feet by 8 feet, you will need approximately 8-12 cubic feet of soil to provide adequate nutrients and drainage. Soil composition should include a mix of topsoil, compost, and potting soil to enhance aeration and water retention, which is vital for plant health. Maintaining this soil volume standard not only supports plant vitality but also improves overall garden productivity throughout the growing season.
Accessibility Height
An accessible garden bed is typically designed at a height of 24 to 36 inches, ensuring ease of use for individuals with limited mobility. These raised beds can be built from materials such as wood, metal, or composite, accommodating various landscaping styles while promoting ergonomic gardening practices. Implementing a width of 3 to 4 feet allows you to reach all areas without straining, making it user-friendly for seated or standing gardeners. Accessible garden beds also often incorporate sturdy side supports for added stability, making gardening an inclusive activity for everyone.
Plant Spacing Suitability
When planning your garden bed, consider the recommended plant spacing to maximize growth and yield. A general guideline is to space plants 12 to 24 inches apart for larger varieties, while smaller crops can thrive with just 6 to 12 inches between them. Proper spacing enhances air circulation, reduces disease risk, and ensures each plant has access to adequate sunlight and nutrients. By following these spacing standards, you can optimize your garden's overall productivity and health.
Drainage Accommodation
A garden bed's drainage capacity is crucial for maintaining healthy plant growth, as over-saturation can lead to root rot and poor nutrient uptake. Ideally, the soil mixture should consist of 50% organic matter and 50% mineral aggregates to enhance water retention while facilitating drainage. Incorporating a layer of gravel or small stones at the bottom of the bed can further improve drainage efficiency, preventing waterlogging. Regular monitoring of moisture levels, aiming for a balanced consistency, ensures optimal conditions for your plants.
Material Options
The selection of materials for garden beds significantly impacts their durability, aesthetics, and sustainability. Common options include cedar, which naturally resists rot for approximately 15-20 years, and corrugated metal, known for its long lifespan and modern look. Moreover, using recycled plastic lumber can promote environmental responsibility while ensuring minimal maintenance. Choose a material that aligns with your gardening goals, available budget, and desired longevity for optimal results.
Climate Adaptation
A climate-adapted garden bed typically features materials such as locally sourced, untreated wood or recycled composites to minimize carbon footprint. By incorporating native plants, which require less water and are more resilient to local climate variations, you can significantly enhance biodiversity and ecosystem health. Implementing a raised bed design can improve drainage and reduce soil compaction, benefiting root growth and microorganism activity. To optimize your planting schedule, consider the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which classifies regions and aids in selecting appropriate species for your climate conditions.
