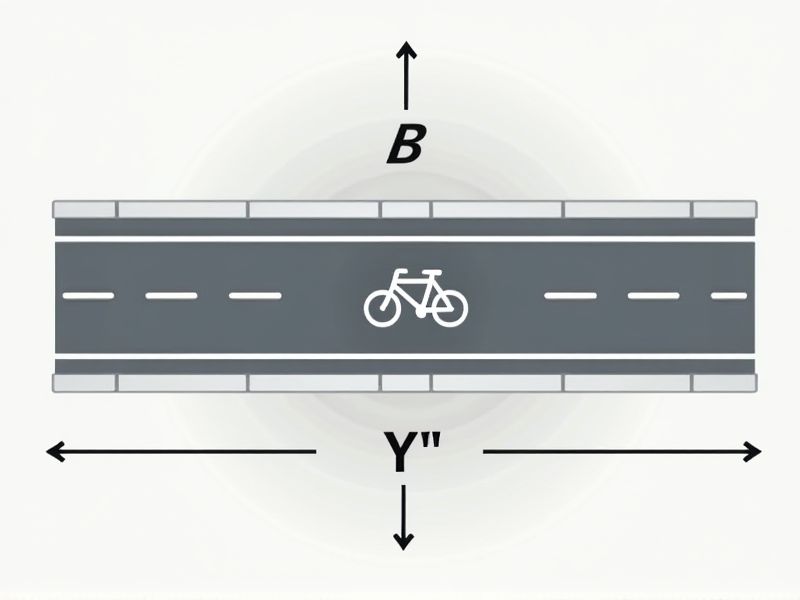
Standard bike lane dimensions vary depending on local regulations, but generally, bike lanes are 4 to 6 feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters) wide. A minimum width of 5 feet (1.5 meters) is often recommended for urban areas to comfortably accommodate one cyclist while allowing for some movement. Wider lanes, around 6 feet, provide extra safety, especially on roads with high speeds or heavy traffic. Always check your city or state's transportation guidelines for the most accurate and up-to-date requirements for bike lane design.
Width
The standard width for a bike lane typically ranges from 1.2 to 1.8 meters, depending on the location and expected cyclist traffic. Wider bike lanes, around 1.5 meters, are recommended in urban areas with higher volumes of cyclists or where overtaking may occur. In contrast, rural or less-trafficked zones may maintain narrower lanes, closer to the 1.2-meter standard. You should consider local guidelines and traffic conditions to ensure optimal safety and usability for all cyclists.
Length
The standard bike lane width is typically 1.5 to 2 meters, providing ample space for cyclists to ride safely. In urban areas, bike lane lengths can vary significantly depending on city planning, with major cities boasting over 300 kilometers of dedicated bike lanes. Studies show that cities with longer bike lane networks experience a 30% increase in cycling rates. Investing in extended bike lane lengths not only enhances cyclist safety but also promotes eco-friendly commuting options for your daily travels.
Lane Markings
Lane markings play a crucial role in the functionality and safety of bike lanes, providing clear visual cues for cyclists and motorists. In 2023, the standard widths for bike lane markings typically range from 4 to 6 inches, ensuring they are visible from a distance. The use of innovative paint materials enhances durability, with some municipalities adopting reflective or thermoplastic options to improve visibility during low-light conditions. Consistent lane markings can reduce accidents by up to 40%, promoting safer cycling environments for urban commuters.
Buffer Zones
Buffer zones in bike lane design promote safety and improve the cycling experience, typically ranging from one to five feet wide. These zones act as a physical barrier between cyclists and motor vehicles, reducing the likelihood of accidents and enhancing rider confidence. Studies indicate that cities with well-designed buffer zones experience a 50% decrease in cyclist injuries. Implementing adequate buffer zones not only protects cyclists but also encourages more individuals to choose biking as a viable transportation option.
Surface Material
The standard surface material for bike lanes typically includes asphalt, concrete, or specialized polymer surfaces, each selected for durability and safety. Asphalt is favored for its smoothness and cost-effectiveness, making up approximately 70% of bike lane installations in urban areas. Concrete offers superior longevity and low maintenance, often used in high-traffic zones where increased stability is essential. Specialized polymer surfaces, like those used in protected bike lanes, enhance traction and provide a comfortable ride, addressing both cyclist safety and performance.
Grade And Slope
The standard for bike lanes emphasizes a maximum slope of 5%, ensuring a comfortable and safe ride for cyclists. Integrating a gentle grade enhances accessibility, particularly for less experienced riders or those on cargo bikes. In urban environments, maintaining a consistent gradient is crucial for promoting bike lane usage, significantly impacting overall cyclist safety and satisfaction. You'll find that adhering to these standards contributes to better traffic flow and encourages more individuals to choose biking as a viable transportation option.
Sight Distance
The standard for bike lanes emphasizes clear sight distance, typically recommending a minimum of 200 feet of visibility to ensure rider safety. This distance allows cyclists to react promptly to oncoming vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles. Proper sight distance is crucial at intersections and curves, where reduced visibility can lead to accidents. For optimal safety, you should ensure that vegetation, signage, and other obstructions are maintained to maintain these visibility standards.
Intersection Design
Bike lane standards emphasize the importance of intersection design to enhance safety and usability. Properly designed intersections account for approximately 40% of bicycle crashes, making it crucial to implement dedicated bike signals and visibility measures. Research indicates that the inclusion of bike boxes can decrease conflicts between cyclists and motor vehicles by up to 60%. By prioritizing user-friendly features like clear signage, adequate lighting, and well-marked lanes, cities can create safer environments for cyclists at critical junctures.
Curve Radius
The standard for bike lane design emphasizes the importance of curve radius, which is crucial for maintaining cyclist safety and comfort. A minimum curve radius of 30 feet is generally recommended to ensure smooth turns and reduce the risk of falls. Research indicates that sharper curves can lead to higher accident rates, underscoring the importance of careful planning in urban environments. When designing bike lanes, consider your local regulations and guidelines, which may vary but typically endorse these curvature standards to promote safe cycling experiences.
Drainage
Proper drainage is crucial for bike lanes, ensuring safety and usability during wet conditions. Effective drainage systems can reduce water accumulation, which helps maintain a clear and dry pathway, optimizing cyclist comfort. Typically, a slope of 1-2% is recommended for bike lanes to facilitate drainage without compromising the lane's usability. Regular maintenance, such as clearing debris from drains, is essential to uphold these drainage standards and protect cyclists from hazards.
